Special Tool: Belt Tension Gauge PV-43532
| IMPORTANT |
| Perform this procedure to achieve proper belt tension and alignment. Belt tension should
be set before performing alignment procedure. |
 WARNING WARNING |
| A drive belt that is not properly tensioned can cause drive line
noise and damage the drive belt, causing possible belt failure
and loss of control of the
motorcycle. |
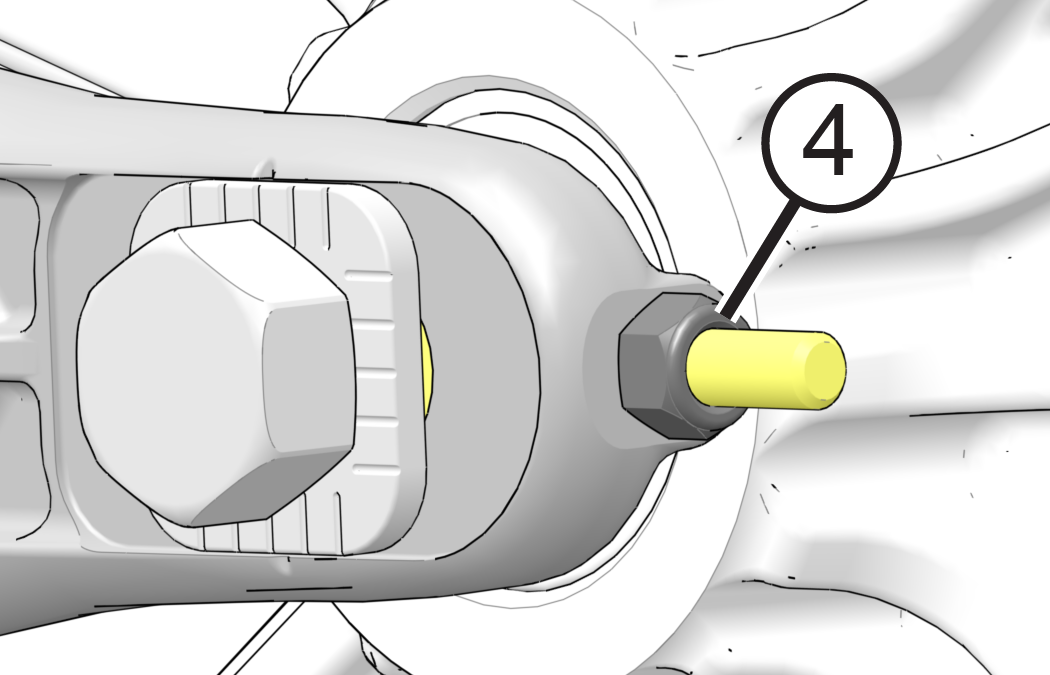
- Inspect drive belt
for damage and wear.
- Ensure rear wheel
is elevated before checking tension or adjusting.
- Use tire valve stem
as a reference and perform following steps:
- Check/record belt
deflection at 4 different points, 90° apart. Rotate wheel in a COUNTER-CLOCKWISE
rotation as viewed from
belt side of motorcycle.
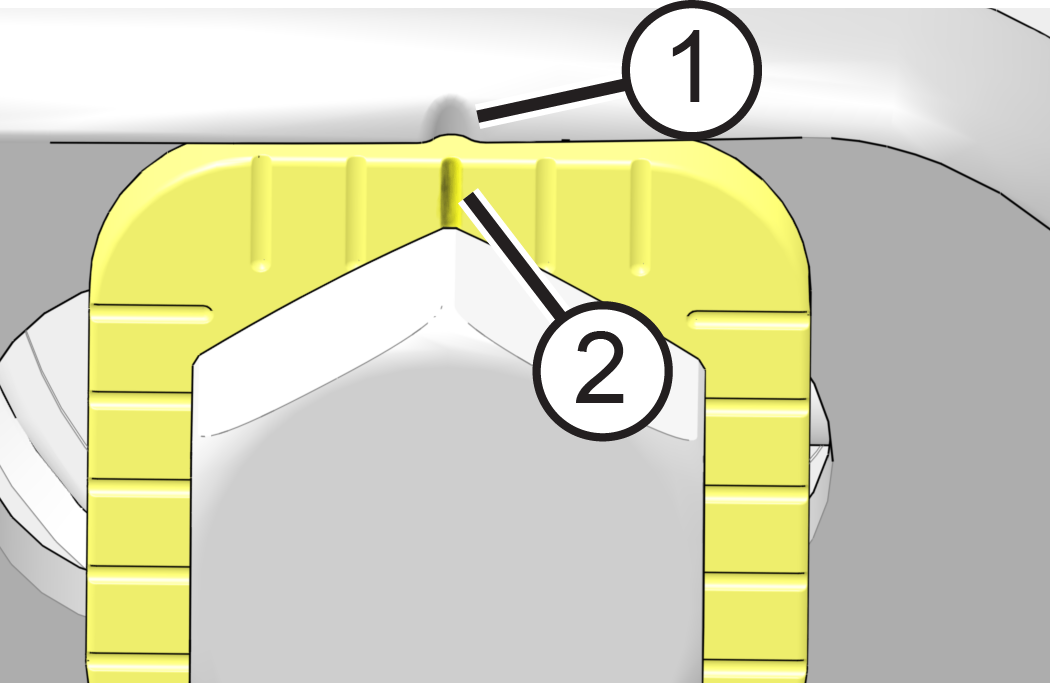
- Place a mark on rear
wheel at tightest point (least deflection) to use as a reference.
- Continue to rotate
wheel in normal drive direction (COUNTER-CLOCKWISE) 1–2 revolutions
until your reference mark (tightest
point) is lined up with tension
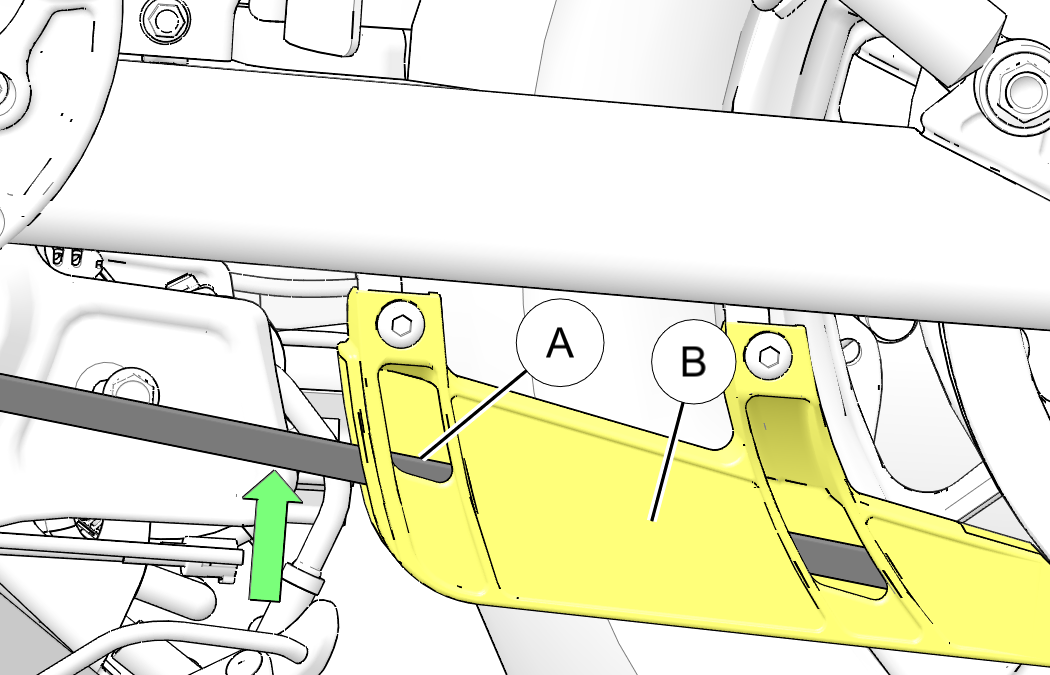
setting window in lower belt guard.
- Adjust belt deflection
with wheel in this position.
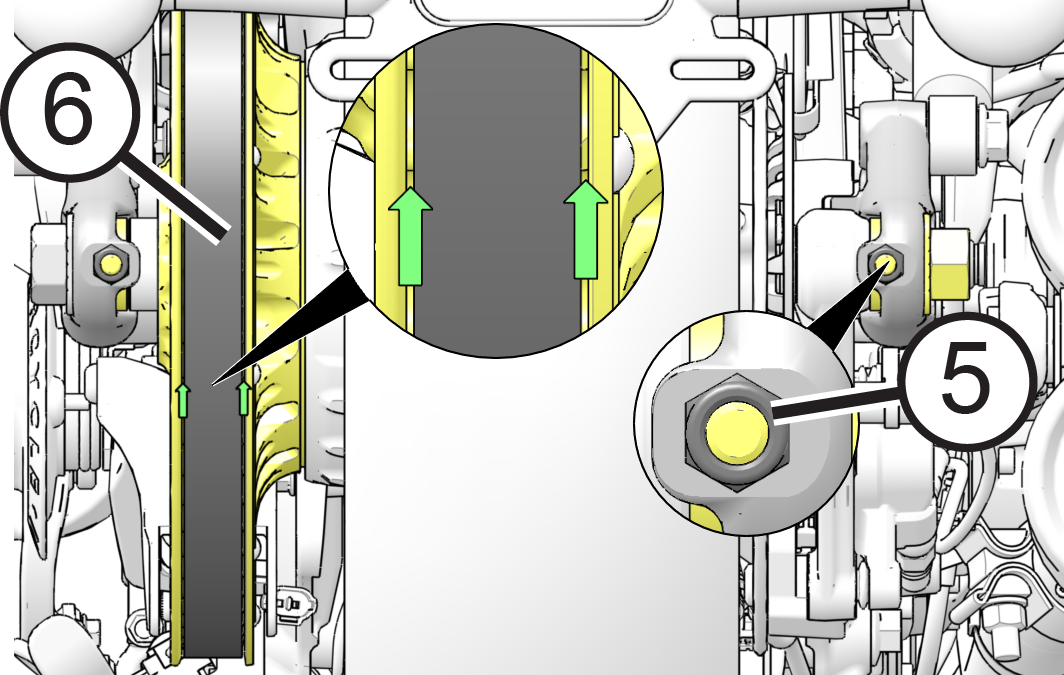
- Place tape measure
or ruler next to drive belt.
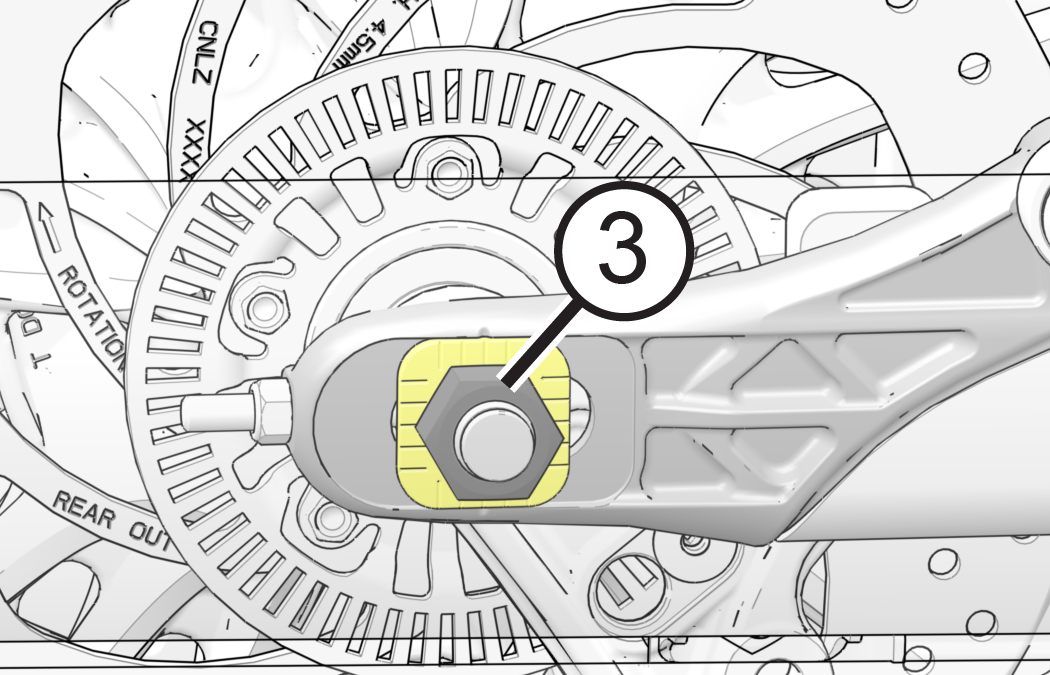
- Slide O-ring on belt
tension gauge to 10 lb. mark.
- Place belt tension
gauge (Special tool PV-43532) squarely against belt at center and
keep it at a 90° angle to the belt surface.
- Push up on gauge
until O-ring just touches tool body and compare to specification.
| MEASUREMENT |
|
Drive Belt Deflection @ 10 lbs force:
12 mm (15/32 in) |
- If belt deflects
more than specified distance with 10 lbs. of force, proceed to Drive Belt Adjustment section
and tighten belt. If belt deflection is less than specified, proceed
to Drive Belt Adjustment section and loosen belt. If belt deflection is correct, lower motorcycle.